Manufacturing Tips for Quality Plastic Assemblies
Quality plastic assemblies often rely on press fits to hold parts in perfect alignment. These bonded interference fits used in assembly connections provide consistent performance
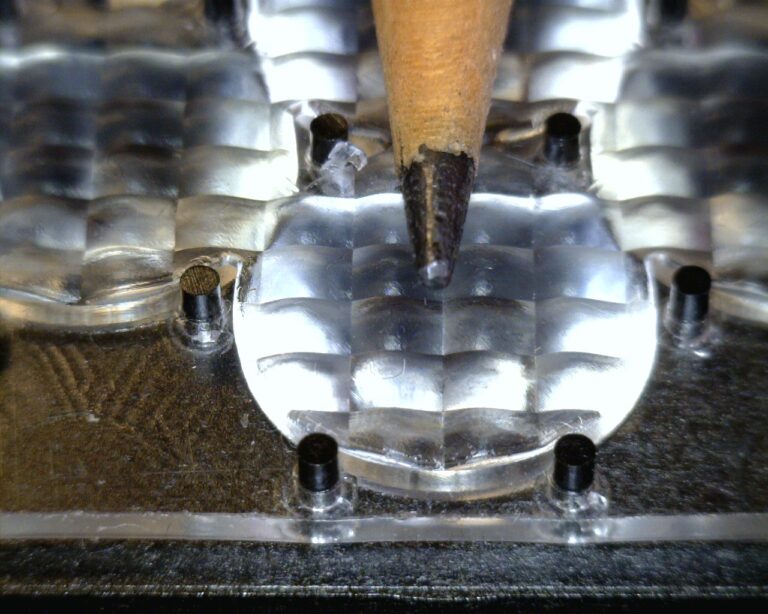
Heat staking is a process used to join two or more components, typically thermoplastics, by applying heat and pressure to deform and fuse the materials. In this process, a heated tool (stake) is used to melt a plastic stud or post, which then forms a mechanical joint as it cools and solidifies. Heat staking enables strong mechanical bonds, versatility with different materials, cost-effectiveness, clean and efficient processes, design flexibility, consistent quality, and environmental resistance.
Examples of Parts
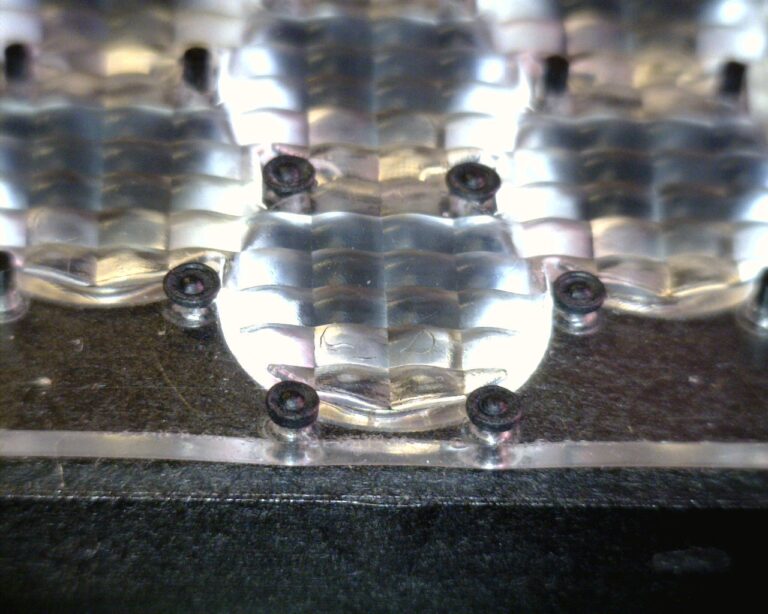
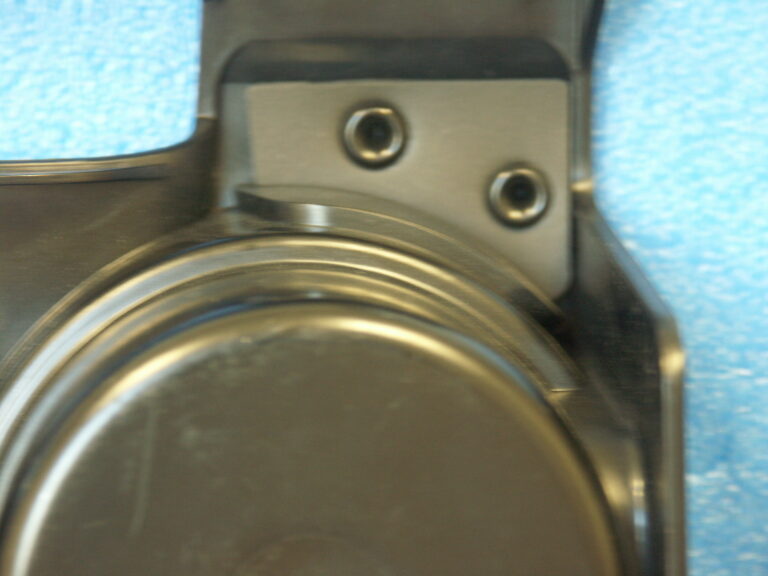
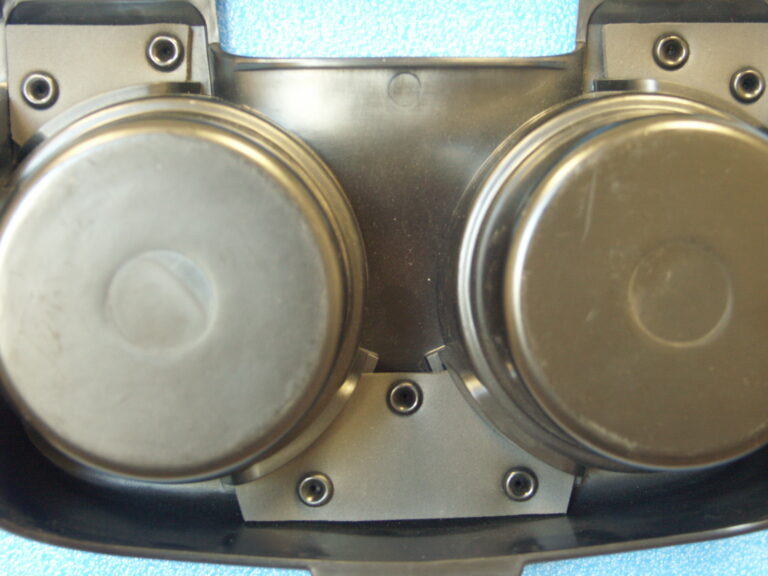
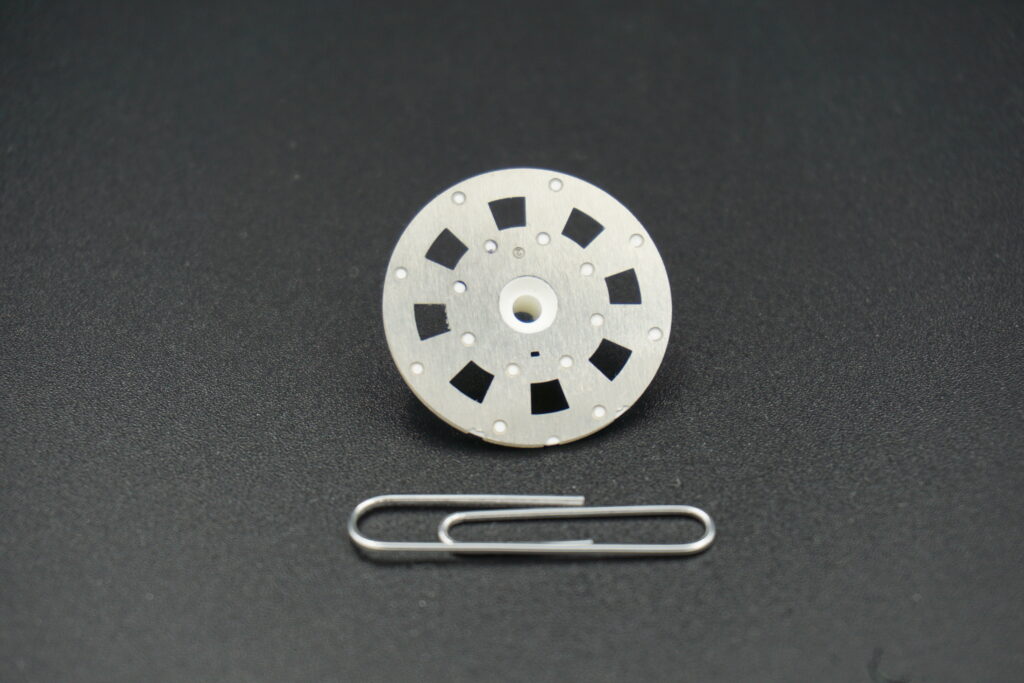
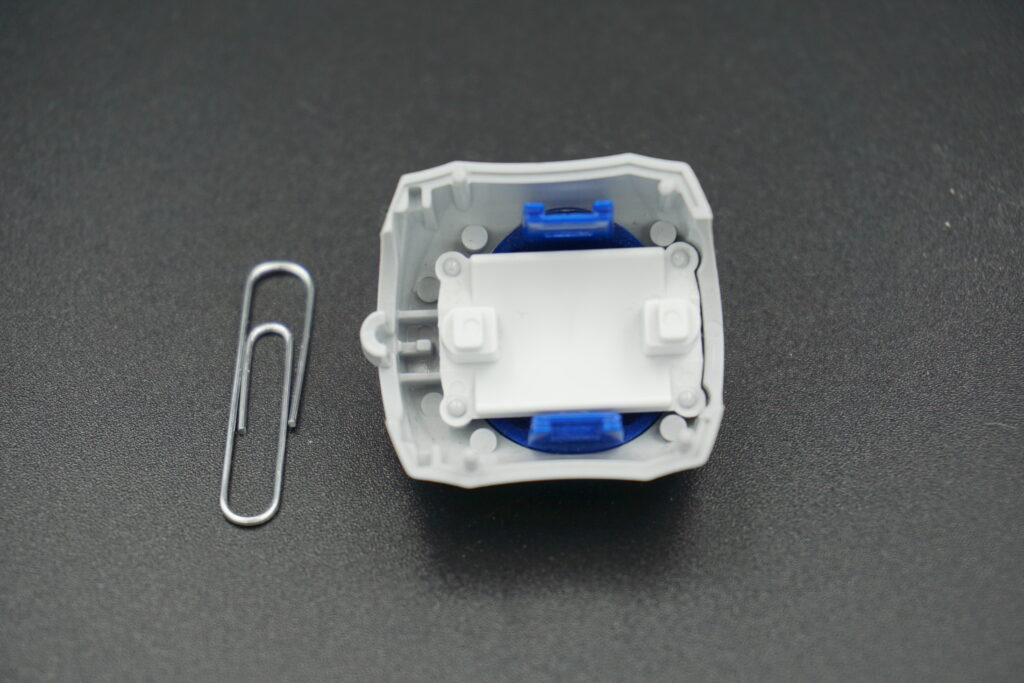





Quality plastic assemblies often rely on press fits to hold parts in perfect alignment. These bonded interference fits used in assembly connections provide consistent performance
Heat staking stands as a fundamental process in modern manufacturing, offering a reliable means to mechanically lock thermoplastic components in place through controlled heating and
Plastics are widely used in modern product designs due to their versatility, low cost, and superior performance characteristics. Compounds like acetals, polypropylenes, and polyethylenes offer
Since its inception in 1976, Thermal Press International (TPI) has consistently set the benchmark in the industry for cutting-edge heat staking equipment and solutions. Offering
This video showcases our C-Series machine, designed to heat stake an iron faceplate for a card reader. The setup includes a power shuttle table, providing efficient and easy loading and unloading of the part for streamlined operation.
This video features an H-Series Thermal Press utilizing a power shuttle table to streamline the loading and unloading of an LED lighting fixture. It is equipped with a custom clamping system to ensure accurate positioning on every run.
This video showcases our C-Series machine, engineered to heat stake a single post on a delicate surgical device. The system features a custom nest and clamping mechanism to ensure precise alignment with every run. Additionally, it includes a power shuttle table for smooth, efficient loading and unloading, optimizing the overall workflow.
This video showcases our C-Series machine heat staking two small automotive components with split level posts simultaneously on a rotary table. The system is equipped with a customized nest and clamping device to ensure precision and accuracy on every run.
This video highlights TPI’s expertise in accurately heat staking a microfluidic diagnostic test card with seventeen extremely small posts. The system features a customized nest and clamping device to ensure precision on every run. Additionally, it incorporates a rotary table for easy loading and unloading, as well as increased production capacity.