Port sealing plays a critical role in the performance, safety, and reliability of many medical, bioengineering, and fluid-handling products.
Heat sealing is a proven method for creating strong, hermetic bonds between thermoplastic components, particularly when sealing ports, fitments, and dispensing features into flexible bags, films, and laminating materials.
From medical fluid bags and diagnostic devices to food and consumer packaging, manufacturers rely on controlled heat and pressure to achieve repeatable, validated seals – even when part geometry, material stacks, or compliance requirements make other joining methods impractical.
This article explores how port sealing works, where heat sealing excels, and what manufacturers should consider when designing tooling and processes for high-reliability applications.
Where Port and Heat Sealing are Used
Heat sealing is widely used to join thermoplastic components in applications where strength, cleanliness, and reliability are critical. Common examples include heat seal connectors for LCD displays and PCBs, thermally activated adhesives for display and enclosure assemblies, and film or foil sealing for medical trays, test devices, and packaging.
In the medical field, heat sealing is frequently used to bond filter media, films, and laminated materials used in diagnostic devices, blood testing products, and sample collection systems. These applications demand controlled heat and pressure to create consistent, contamination-free seals without damaging sensitive materials.
Port Sealing in Medical and Fluid Bag Applications
A growing market for heat sealing applications over the last decade is in the manufacture of medical and fluid bags used in the medical, bioengineering and food industries. Fluid bags are made out of a multitude of varying materials such as foils, filter media, thermoplastics and laminates. Material selection for the bags is based upon their intended application or compliancy requirements.
Medical bags are used in an array of applications, from the dispensing of medicine to the collection or transfer of blood or other biological media. The usage of these fluidic bags and the flexibility they have provided has been expanding into the consumer products and food industries over the last decade.
The growth of the converting and laminating equipment technologies and processes have created many exciting new opportunities for the production of new films and laminates used to make medical and fluid bags. The laminated films and bag materials specifically are engineered to have very colorful print options and artwork on the outside layer, while having food or medical compliancy properties for the internal material and structure of the bag. This provides manufacturers and food producers with new delivery and marketing opportunities for their food and liquid products.
Ports, Fitments, and Sealing Configurations
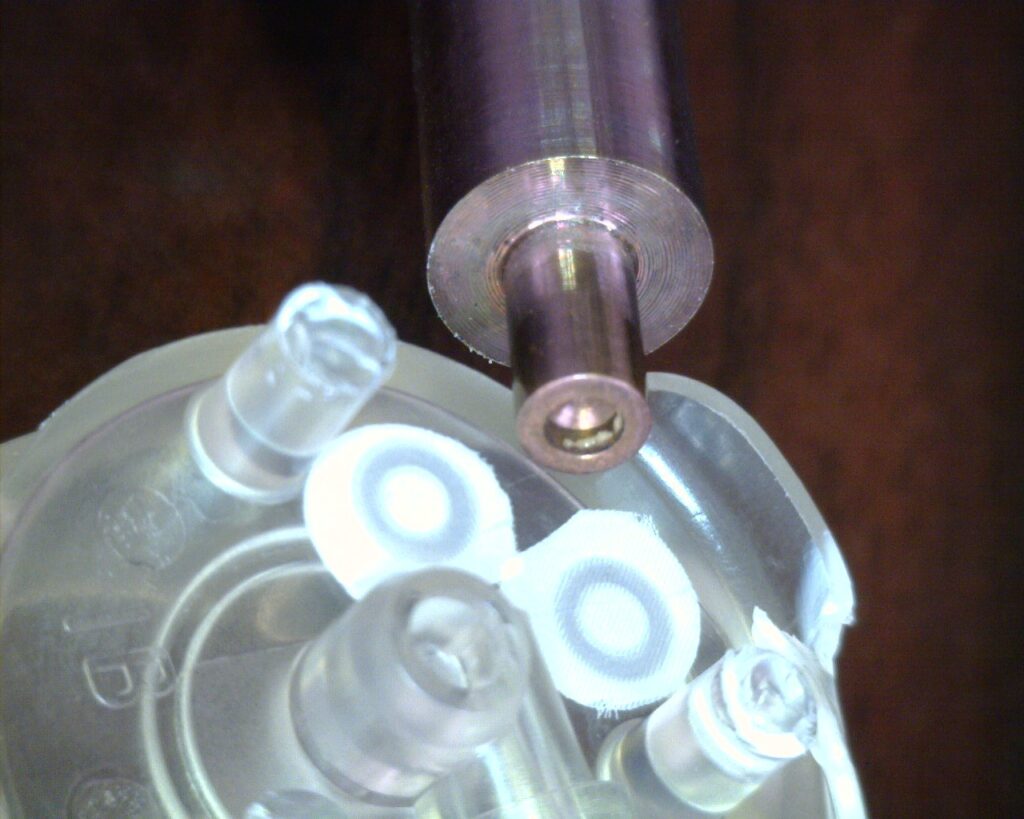
One feature these fluid bags have in common is the need to have ports for getting fluids in and/or out of the bags. Ports, tubes or fitments are installed and heat sealed or welded into the bags. The ports, tubes and/or fitments for these bags most often are attached with the heat sealing and RF welding technologies, but impulse and ultrasonic welding also are commonly used. The heat sealed ports must have a hermetic seal.
Plastic ports and fittings that are sealed onto the media bags also often are called port plates, port discs, end dispensing fitments or boat fitments. These various ports and fitments are manufactured by injection mold companies worldwide and are readily available in standard shapes, styles and sizes. Flanged port plates with barbed port for tube installation are available from 3/16″ to 1″. Dual barbed ports also are available for applications that require tubes inside and outside of the bag. Ports with screw cap and other dispensing configurations are available.
Boat fitments or end dispensing fitments are wedge-like pieces that are sealed into an open end of a bag. Boat fitments usually have multiple ports for multiple tubes or connectors. Custom port configurations and/or custom boat fitments can be manufactured by an injection molder to meet any specific engineering or manufacturing requirement.
Tooling, Fixturing, and Process Control Considerations
The heat sealing process for ports requires a heat seal die or blade designed to work with the specific port or fitment. The port usually is located over a mandrel or fixture during the heat sealing process. Heat sealing usually is performed with the bag or film material over the port while it is on the mandrel or fixture. There also usually is a layer of interposer material to prevent sticking between the heat seal die and the film material during the heat sealing process.
Some port heat sealing applications require an engineered material to be underneath the port to act as a back stop or heat sink for the heat sealing process. The back stop material can be a compliant- and/or a silicone-based material. This will allow the thermal conductivity of the die to pass the heat through the film or bag material and through the flange of the port, while squeezing the parts together to achieve a hermetic heat seal. Material selection for the back stop must be selected based upon heat seal testing of the bag and port materials selected.
The ports and fitments are installed either on an open or closed bag. The tooling and heat seal process for an open bag or single-layer film is the simplest when compared to other applications. The tooling can be an open or flat format with just a part location feature. Closed bags are more complicated and require some sort of knee or mandrel that allows the bag to be placed over it to locate the entire bag relative to the port location to be heat sealed.
End dispensing or boat fitments require heat sealing into the end of a closed bag requiring multiple mechanisms and heat seal dies. The heat seal tooling for the end dispensing or boat fitments usually requires heat sealing completely around the fitment or around the open end of the bag from both sides during a single cycle. Sometimes, this heat seal is performed while sealing the entire perimeter of the bag itself.
Since many of the bag applications are for storing medical fluids or dispensing medicine, a higher level of assembly equipment and validation of the heat seal processes are required. When a higher level of accuracy is required, then the heat seal equipment must have an appropriate level of validation and control features. Heat sealing systems with linear or servo actuators integrated into the machine along with process control alarms have the highest ratings for accuracy and repeatability.